CESNET has developed a technology for detecting vibrations on the fiber infrastructure; successful tests took place on the ČD -Telematika network
Prague, January 17th, 2022. As part of its research activities, the CESNET Association developed a sensor system to detect possible damage to the fibre infrastructure and experimentally verified its concept on a real route in cooperation with ČD – Telematika.
“Protecting the fibre infrastructure from possible damage, whether accidental or intentional, is absolutely essential for the security of data transmissions. The developed system can be a suitable enhancement of the security of guaranteed key transfer methods, such as QKD (Quantum Key Distribution). For this reason, we are working on the development of methods, procedures and hardware sensor devices for the early detection of undesirable anomalies in the fibre infrastructure, which will enable a rapid and adequate response of network operators, “says Josef Vojtěch, Head of the CESNET Optical Networks Department.

Fig. 1: Map of the leased route Žďár nad Sázavou-Křižanov-Tišnov including marked measuring sections
“The ČD – Telematika optical network is particularly suitable for such projects due to its size and robustness. And the deployment of our highly qualified staff has guaranteed both the completion of the project on time and the proof of results so important for the subsequent commercial use of the tested technology, “emphasizes Jan Bartoš, Head of the ČD – Telematics Sales Department. “We have been supporting research in this area for over twenty years and we support Czech science either by cooperating on specific projects or by sharing the experience of our telecommunications team,” adds Jan Bartoš.
In 2020, in cooperation with ČD – Telematika, CESNET deployed a sensor system within the DOBI project (Infrastructure Security Threat Detection) for long-term measurements on the real route between Tišnov and Žďár nad Sázavou. The measurements took place in two sections: between Tišnov and Řikonín (occurrence of several mining quarries) and between Křižanov and Žďár along the railway line, where the track and surrounding buildings were reconstructed (see Figure 1). This allowed the detection of strong vibrations in the field and their subsequent analysis.
The measurements were carried out using a prototype sensor system. The system is mechanically robust and has low power consumption. Measurement by sensing changes in polarization is also low on light source parameters and quite common and inexpensive Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers can be used with advantage. In addition, a conventional data transmission signal can also be used as a measurement source. Only approx. 2% of the optical power needs to be tapped using an optical tap.
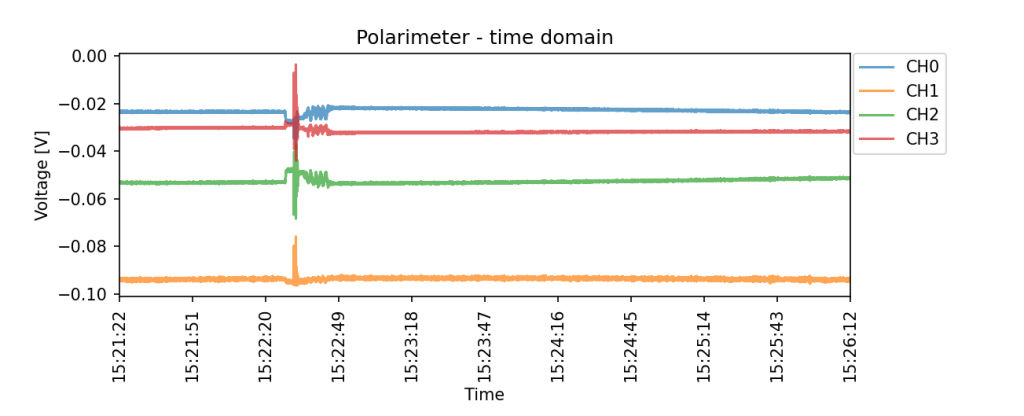
The sensor device made it possible to continuously monitor the state of polarization of light in the optical path. The measured data can be processed both continuously for rapid detection of significant anomalies and later in batches within advanced analysis, including the involvement of algorithms and artificial intelligence methods. An example of an object with an unwanted fiber manipulation anomaly is shown in Figure 2.
Fig. 2: Measured values of light polarization changes in the optical path with the occurrence of an interference event at approximately 15:22:30
The deployed prototype of the sensor system verified the applicability of the selected technology and procedures in practice. Based on the knowledge gained during the development and testing of the prototype sensor system, the Polarilog device was developed. It is a small and compact device that can be deployed on any line where there are concerns about tampering and the security of transmitted data. The main advantages include the ability to use the existing infrastructure with minimal additional hardware, including the ability to use existing data traffic for measurement. In addition, with an appropriate system configuration, it is possible to detect the location of the event where the fibre is manipulated or in the vicinity of acoustic-mechanical vibrations. Detectable events include, for example, direct manipulation of the fibre itself or a patchcord on the route, train passage, excavation work, etc. The solution used has considerable potential in the deployment of automated processing and artificial intelligence, which will allow, for example, independently identifying certain categories of critical events, and thus enabling operators to better respond to security threats.
The video demonstrates the possibility of detecting fiber manipulation by sensing changes in the state of polarization in the optical fiber:


The CESNET association was founded in 1996 by universities and the Czech Academy of Sciences. It is engaged in research and development of information and communication technologies, building and developing a national CESNET e-infrastructure for research and education. Thanks to its research activities and achievements, it represents the Czech Republic in important international projects, especially in building the pan-European network GÉANT or grid projects (EGI.eu), and participates actively in their implementation. The association is also working on the use of high-speed networks for sharing multimedia data, both synchronously in the form of video conferencing and shared applications, and asynchronously in the form of streaming. Since December 2020, CESNET represents the Czech Republic in the international association dealing with the open science paradigm – EOSC AISBL. More at: www.cesnet.cz
ČD – Telematika a.s. is a major provider of railway security and communication technologies and a supplier of wholesale telecommunications services and services in the area of management, maintenance and construction of optical infrastructures. It operates its own optical network in the Czech Republic, which is part of the key infrastructure of the state. It complements its portfolio of activities with value-added services in areas such as road telematics. More at: www.cdt.cz
